As a head protection device, safety helmets can effectively prevent and reduce injuries to workers' heads caused by falling objects and personal falls during production operations. 15% of falling object injury accidents are attributed to improper use of safety helmets.

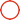
1.Structure of Safety Helmet
Shell: Bears external impacts and isolates falling objects from the human body.
Hatband: Maintains the helmet in a fixed position on the head.
Suspension strap: Distributes impact force and allows shell floating to disperse energy.
Adjustable buckle: Locking device for the headband.
Chin strap: Assists in stabilizing the helmet's position.
Cushion: Reduces impact force during collisions.
Adjustment Before Wearing
Adjust the rear adjustment strap to fit your head shape.
Secure the elastic inner strap and adjust the tightness of the cushion pad via the adjustment strap.
Maintain a vertical clearance of 25-50mm (minimum ≥32mm) between the top of the head and the helmet’s inner shell. This ensures sufficient buffer space during impacts and improves ventilation.

Correct Positioning
Avoid tilting the helmet or wearing it backward (e.g., with the brim facing the back of the head), as this compromises impact resistance.

Securing the Chin Strap
Fasten the chin strap securely under the jaw with moderate tightness.
Ensure it stays fixed during strong winds, collisions, or head movements to prevent the helmet from falling off.
Inspection of New Helmets
When receiving a new safety helmet:
Verify it carries labor department approval certification and a valid product qualification certificate.
Check for defects: cracks, uneven thickness, or damaged components.
Ensure the impact-absorbing layer, adjustment straps, and elastic bands are fully functional and intact.
Replace immediately if any non-compliance is detected.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 